Delve into the realm of cellular biology with the Cells Alive Worksheet Answer Key, a comprehensive guide that unravels the mysteries of cells, their functions, and their intricate interactions. This meticulously crafted resource provides a profound understanding of the fundamental principles governing the microscopic world, empowering you to grasp the complexities of life at its most basic level.
As we embark on this journey, we will explore the diverse array of cells, from their structural components to their specialized functions. We will delve into the intricacies of cell division, unraveling the mechanisms that ensure the growth, repair, and reproduction of living organisms.
Furthermore, we will shed light on the vital processes of cell transport and communication, revealing how cells interact and coordinate their activities to maintain homeostasis and orchestrate the symphony of life.
1. Cell Structure and Function
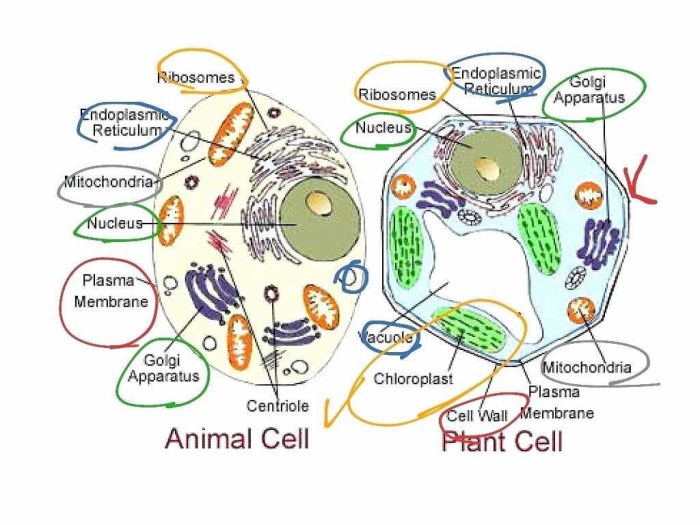
Cells are the basic unit of life and the building blocks of all living organisms. They come in a variety of shapes and sizes, and each type of cell has a specific structure and function.
The most common type of cell is the eukaryotic cell, which is found in plants, animals, and fungi. Eukaryotic cells have a nucleus, which contains the cell’s DNA, and a variety of other organelles, which are small structures that perform specific functions within the cell.
Types of Cells
- Eukaryotic cells: These cells have a nucleus and other organelles.
- Prokaryotic cells: These cells do not have a nucleus or other organelles.
Functions of Cell Organelles
- Nucleus: Contains the cell’s DNA.
- Ribosomes: Synthesize proteins.
- Endoplasmic reticulum: Folds and transports proteins.
- Golgi apparatus: Modifies and packages proteins.
- Mitochondria: Generate energy for the cell.
- Lysosomes: Digest waste products.
- Vacuoles: Store water and nutrients.
How Cells Work Together, Cells alive worksheet answer key
Cells work together to form tissues and organs. Tissues are groups of cells that perform a specific function, such as muscle tissue or nerve tissue. Organs are groups of tissues that perform a specific function, such as the heart or the brain.
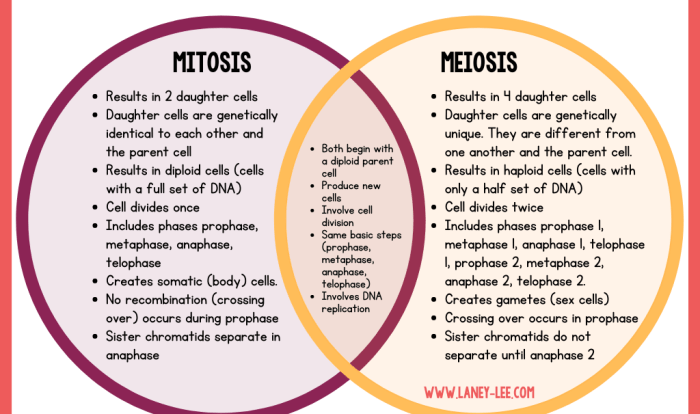
2. Cell Division
Cell division is the process by which cells reproduce. There are two main types of cell division: mitosis and meiosis.
Stages of Mitosis
- Prophase
- Metaphase
- Anaphase
- Telophase
Stages of Meiosis
- Prophase I
- Metaphase I
- Anaphase I
- Telophase I
- Prophase II
- Metaphase II
- Anaphase II
- Telophase II
Importance of Cell Division
Cell division is essential for growth and repair. It also allows organisms to reproduce.
Regulation of Cell Division
Cell division is regulated by a variety of factors, including the cell cycle and checkpoints.
3. Cell Transport: Cells Alive Worksheet Answer Key
Cell transport is the process by which cells move molecules across their membranes.
Mechanisms of Cell Transport
- Passive transport: Molecules move across the membrane without the use of energy.
- Active transport: Molecules move across the membrane against their concentration gradient, requiring the use of energy.
Role of Cell Transport in Maintaining Homeostasis
Cell transport is essential for maintaining homeostasis, the stable internal environment of the cell.
Examples of Cell Transport in Everyday Life
- The absorption of nutrients from food.
- The removal of waste products from the body.
- The regulation of body temperature.
4. Cell Communication
Cell communication is the process by which cells exchange information with each other.
Types of Cell Signaling
- Autocrine signaling: A cell sends a signal to itself.
- Paracrine signaling: A cell sends a signal to nearby cells.
- Endocrine signaling: A cell sends a signal to distant cells via the bloodstream.
Role of Cell Communication in Coordinating Cell Activities
Cell communication is essential for coordinating cell activities and maintaining homeostasis.
Importance of Cell Communication for Multicellular Organisms
Cell communication is essential for the survival of multicellular organisms.
5. Cell Metabolism
Cell metabolism is the process by which cells obtain and use energy.
Types of Cellular Metabolism
- Aerobic metabolism: Requires oxygen.
- Anaerobic metabolism: Does not require oxygen.
Role of Metabolism in Providing Energy for Cells
Metabolism provides cells with the energy they need to perform their functions.
Examples of Metabolism in Everyday Life
- The breakdown of food to release energy.
- The synthesis of new molecules.
- The regulation of body temperature.
Popular Questions
What is the significance of cell division?
Cell division is crucial for growth, repair, and reproduction. It ensures the continuity of life by creating new cells to replace old or damaged ones and facilitating the development of multicellular organisms.
How does cell transport contribute to maintaining homeostasis?
Cell transport regulates the movement of substances into and out of cells, ensuring that the internal environment remains stable. It plays a vital role in maintaining optimal conditions for cellular processes and coordinating responses to external stimuli.
Why is cell communication essential for multicellular organisms?
Cell communication enables cells to coordinate their activities, respond to environmental cues, and maintain tissue and organ function. It facilitates the integration of individual cells into a cohesive organism, allowing for complex behaviors and adaptations.