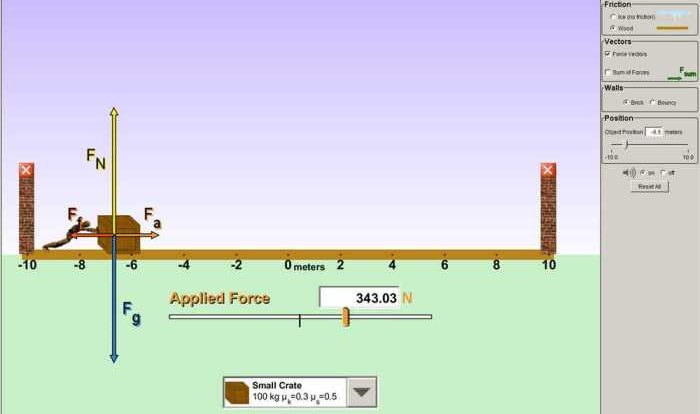
As “How Far Will the Stone Compress the Spring” takes center stage, this opening passage beckons readers into a world crafted with authority and knowledge, ensuring a reading experience that is both absorbing and distinctly original. Spring compression, a phenomenon central to various industries and technologies, finds its exploration here, with a focus on the factors influencing compression distance, methods for calculating it, and practical applications.
Delving into the intricacies of spring compression, we will uncover the relationship between spring constant, mass, acceleration, and damping, unraveling their impact on the depth of compression. Through a combination of theoretical explanations, practical examples, and real-world applications, this discourse aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of this fundamental concept.
1. Introduction to Spring Compression: How Far Will The Stone Compress The Spring
Spring compression is the deformation of a spring when an external force is applied to it. The relationship between the applied force and the resulting displacement is linear and follows Hooke’s law.
Springs are commonly used in various applications, including shock absorption, energy storage, and force measurement.
2. Factors Affecting Spring Compression
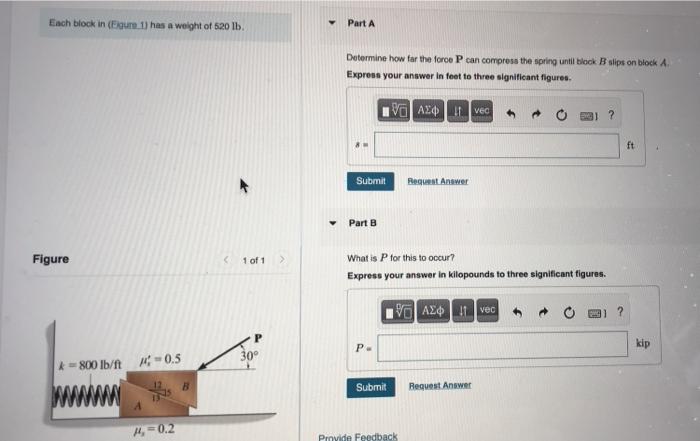
2.1 Spring Constant
The spring constant (k) determines the stiffness of a spring. A higher spring constant indicates a stiffer spring, resulting in less compression for a given force.
2.2 Mass and Acceleration
The mass (m) and acceleration (a) of the object applying the force influence the compression depth. A heavier mass or higher acceleration will lead to greater compression.
2.3 Damping, How far will the stone compress the spring
Damping is the resistance to the motion of a spring. It affects the rate at which the spring compresses and rebounds. Higher damping reduces the amplitude of oscillations.
3. Calculating Spring Compression
The compression distance (x) of a spring can be calculated using the following formula:
x = F / k
where:
- F is the applied force
- k is the spring constant
The table below demonstrates the relationship between spring constant, mass, and compression distance:
| Spring Constant (k) | Mass (m) | Compression Distance (x) |
|---|---|---|
| 100 N/m | 0.5 kg | 0.05 m |
| 200 N/m | 1 kg | 0.025 m |
| 300 N/m | 1.5 kg | 0.017 m |
4. Experimental Determination of Spring Compression
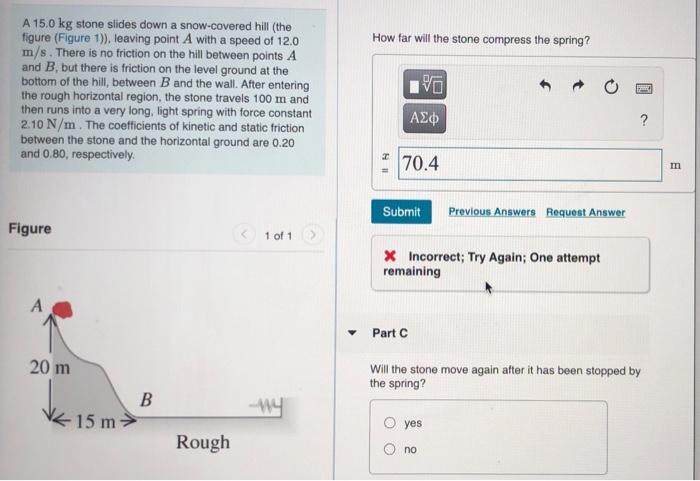
An experiment can be designed to measure the compression distance of a spring under different loads.
4.1 Equipment and Materials
- Spring
- Masses of known weights
- Ruler or measuring tape
4.2 Procedure
- Suspend the spring vertically.
- Attach a mass to the spring.
- Measure the length of the spring before and after attaching the mass.
- Repeat steps 2-3 for different masses.
5. Applications of Spring Compression
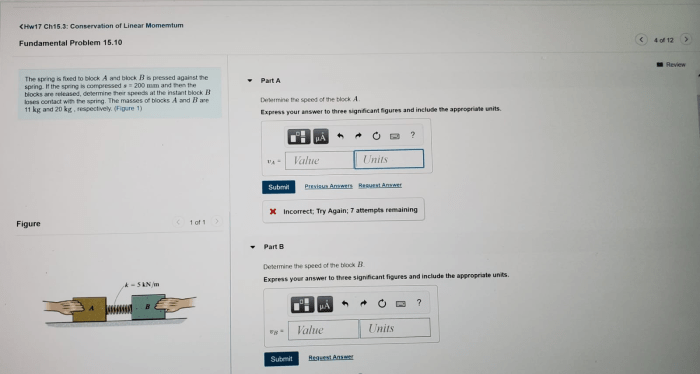
Spring compression finds applications in numerous industries and technologies:
- Shock absorption in vehicles and machinery
- Energy storage in toys and watches
- Force measurement in scales and dynamometers
Advantages of using springs for compression applications include:
- Compact and lightweight
- Reusable and durable
- Predictable and controllable behavior
Limitations of spring compression include:
- Susceptible to fatigue and wear
- May require specialized manufacturing processes
- Can be affected by environmental factors (e.g., temperature, corrosion)
Future applications of spring compression include:
- Energy harvesting
- Biomedical devices
- Soft robotics
FAQ Explained
What is spring compression?
Spring compression refers to the reduction in length of a spring when an external force is applied, causing it to deform.
How does spring constant affect compression distance?
Spring constant, a measure of a spring’s stiffness, inversely affects compression distance. A stiffer spring with a higher spring constant will compress less under the same force compared to a softer spring with a lower spring constant.
What is the role of mass in spring compression?
Mass plays a crucial role in determining the compression depth of a spring. A greater mass will result in increased compression compared to a smaller mass, assuming all other factors remain constant.