Mutation worksheet deletion insertion and substitution – The Mutation Worksheet: Deletion, Insertion, and Substitution provides a comprehensive overview of the different types of gene mutations, their causes, and their consequences. This worksheet is an essential tool for students and researchers alike, providing a clear and concise explanation of this important topic.
The first section of the worksheet introduces the concept of gene mutation and provides examples of deletion, insertion, and substitution mutations. The second section discusses the causes of mutations, including environmental factors, replication errors, and chemical agents. The third section explores the consequences of mutations, including their potential benefits, harmful effects, and neutral effects.
The fourth section provides an overview of mutation detection and analysis techniques.
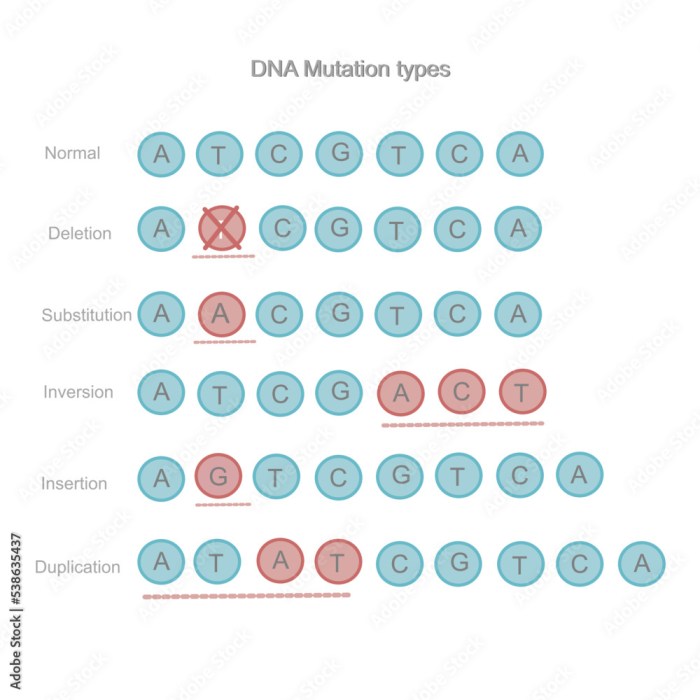
Mutation Types
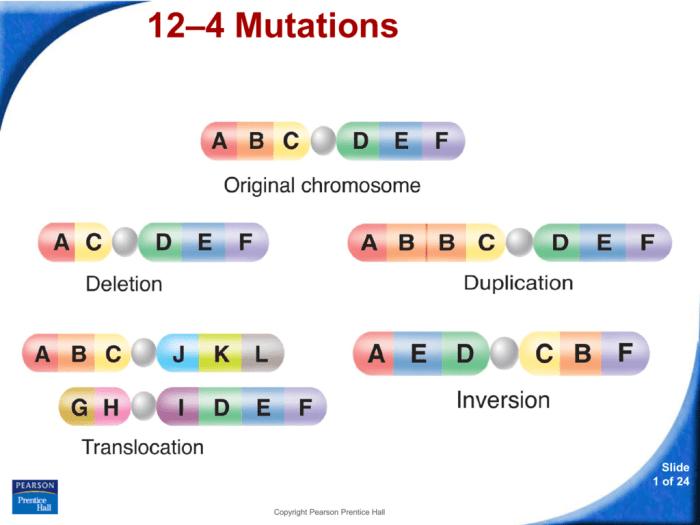
Gene mutations are alterations in the nucleotide sequence of DNA that can affect the structure or function of a gene. They can be classified into three main types:
Deletion Mutations
Deletion mutations occur when one or more nucleotides are removed from the DNA sequence. These mutations can range in size from a single nucleotide to large segments of DNA. Deletions can lead to frameshift mutations, which can disrupt the reading frame of the gene and result in a non-functional protein.
Insertion Mutations
Insertion mutations occur when one or more nucleotides are added to the DNA sequence. These mutations can also range in size from a single nucleotide to large segments of DNA. Insertions can disrupt the reading frame of the gene, leading to frameshift mutations.
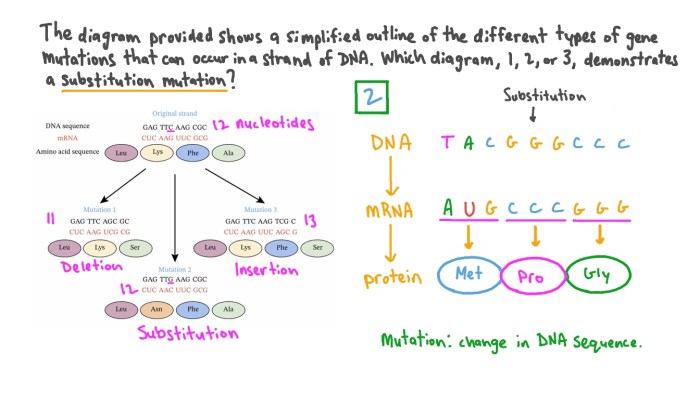
Substitution Mutations
Substitution mutations occur when one nucleotide is replaced by another nucleotide. These mutations can be either silent (not affecting the amino acid sequence of the protein) or non-silent (altering the amino acid sequence). Non-silent substitution mutations can lead to changes in protein structure and function.
Causes of Mutations
Mutations can be caused by a variety of factors, including:
Environmental Factors
Environmental factors, such as ultraviolet radiation and chemical agents, can damage DNA and lead to mutations. Ultraviolet radiation can cause the formation of thymine dimers, which can disrupt DNA replication and lead to mutations.
Replication Errors, Mutation worksheet deletion insertion and substitution
Replication errors can also lead to mutations. During DNA replication, errors can occur in the copying of the DNA sequence. These errors can lead to insertions, deletions, or substitutions in the DNA sequence.
Chemical Agents
Chemical agents, such as alkylating agents and intercalating agents, can also induce mutations. Alkylating agents can add alkyl groups to DNA bases, which can lead to base substitutions. Intercalating agents can insert themselves between DNA bases, which can lead to frameshift mutations.
Consequences of Mutations: Mutation Worksheet Deletion Insertion And Substitution

Mutations can have a variety of consequences, depending on the type of mutation and the gene that is affected.
Benefits of Mutations
Some mutations can be beneficial, as they can lead to new or improved traits. For example, mutations in the lactase gene have allowed humans to digest lactose, a sugar found in milk, into adulthood. This mutation has been beneficial for humans as it has allowed them to access a new source of nutrition.
Harmful Mutations
Other mutations can be harmful, as they can lead to genetic disorders or diseases. For example, mutations in the BRCA1 gene can increase the risk of breast and ovarian cancer. Mutations in the cystic fibrosis gene can lead to cystic fibrosis, a genetic disorder that affects the lungs and digestive system.
Neutral Mutations
Some mutations are neutral, as they do not have any effect on the phenotype of the organism. These mutations are often found in non-coding regions of DNA or in genes that are not essential for the organism’s survival.
Contribution to Genetic Disorders
Mutations can contribute to genetic disorders by altering the structure or function of genes. These alterations can lead to a variety of symptoms, depending on the gene that is affected. Some genetic disorders are inherited, while others can occur spontaneously.
Detection and Analysis of Mutations

Mutations can be detected and analyzed using a variety of techniques.
Mutation Detection Techniques
| Technique | Description |
|---|---|
| PCR | Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) can be used to amplify a specific region of DNA, which can then be sequenced to detect mutations. |
| Sanger sequencing | Sanger sequencing is a method of DNA sequencing that can be used to detect mutations. |
| Next-generation sequencing (NGS) | NGS is a high-throughput DNA sequencing technology that can be used to detect mutations. |
Mutation Analysis Process

Mutation Analysis Software Tools
| Software | Features |
|---|---|
| Mutation Surveyor | Mutation Surveyor is a software program that can be used to detect and analyze mutations. |
| Sequencher | Sequencher is a software program that can be used to analyze DNA sequences and detect mutations. |
| CLC Genomics Workbench | CLC Genomics Workbench is a software program that can be used to analyze DNA sequences and detect mutations. |
Bioinformatics Tools for Mutation Identification
Bioinformatics tools can be used to identify mutations by comparing DNA sequences to reference sequences. These tools can be used to detect a variety of mutations, including SNPs, insertions, and deletions.
Questions and Answers
What is a gene mutation?
A gene mutation is a change in the DNA sequence of a gene. Mutations can be caused by a variety of factors, including environmental factors, replication errors, and chemical agents.
What are the different types of gene mutations?
There are three main types of gene mutations: deletion mutations, insertion mutations, and substitution mutations. Deletion mutations involve the loss of one or more nucleotides from a gene. Insertion mutations involve the addition of one or more nucleotides to a gene.
Substitution mutations involve the replacement of one nucleotide with another.
What are the consequences of gene mutations?
The consequences of gene mutations can vary depending on the type of mutation and the location of the mutation within the gene. Some mutations can be beneficial, while others can be harmful. Some mutations have no effect on the organism.