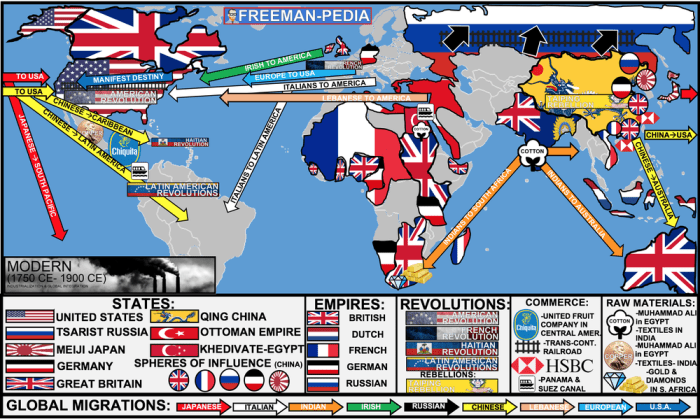
Nationalism and revolutions in the period from 1750 to 1900 – The era from 1750 to 1900 witnessed a profound interplay between nationalism and revolutions, shaping the political, social, and cultural landscapes of the world. This essay explores the complex relationship between these two forces, examining their origins, manifestations, and enduring legacies.
Nationalism, a powerful ideology that emphasizes loyalty to one’s nation, emerged as a dominant force during this period. It inspired movements for independence, sparked revolutions, and fueled imperial expansion. Revolutions, in turn, often drew upon nationalist sentiments to mobilize mass support and challenge established orders.
The Rise of Nationalism

The period from 1750 to 1900 witnessed the rise of nationalism, a powerful force that would shape the political and social landscape of the world. Nationalism is a sense of belonging to a nation, a community of people who share a common history, culture, and language.
It is often accompanied by a desire for political independence and self-determination.
Factors Contributing to the Growth of Nationalism
- The spread of Enlightenment ideas, which emphasized the importance of individual rights and self-government
- The rise of industrialization, which created a more interconnected world and led to the growth of national economies
- The spread of literacy and education, which allowed people to learn about their own history and culture
- The growth of mass media, which allowed nationalist ideas to spread quickly and easily
Different Forms of Nationalism
- Civic nationalism:Based on the idea that all citizens of a nation are equal, regardless of their ethnicity, religion, or social status
- Ethnic nationalism:Based on the idea that a nation is defined by its shared ethnicity or race
- Religious nationalism:Based on the idea that a nation is defined by its shared religion
Influence of Nationalism on Political and Social Movements
- Nationalism inspired the American Revolution (1775-1783), the French Revolution (1789-1799), and the Haitian Revolution (1791-1804)
- Nationalism led to the unification of Italy (1861) and Germany (1871)
- Nationalism inspired anti-colonial movements in Africa, Asia, and Latin America
Revolutions and Nationalism: Nationalism And Revolutions In The Period From 1750 To 1900
Nationalism played a major role in the outbreak of revolutions in the period from 1750 to 1900. Nationalist movements often sought to overthrow existing governments and establish independent nation-states.
Role of Nationalism in Revolutions
- Nationalism provided a sense of unity and purpose for revolutionaries
- Nationalism helped to mobilize mass support for revolutions
- Nationalism inspired revolutionaries to fight for their independence
Comparison of Revolutions
| Revolution | Causes | Goals | Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|
| American Revolution (1775-1783) | British colonial rule, taxation without representation | Independence from Great Britain | Establishment of the United States of America |
| French Revolution (1789-1799) | Absolute monarchy, economic inequality | Overthrow of the monarchy, establishment of a republic | Reign of Terror, rise of Napoleon Bonaparte |
| Haitian Revolution (1791-1804) | French colonial rule, slavery | Abolition of slavery, independence from France | Establishment of the Republic of Haiti |