Why is uneven-aged management a better way to manage forests – As the debate over forest management strategies rages on, uneven-aged management emerges as a compelling alternative, offering a comprehensive solution to the multifaceted challenges facing our forests. This approach, rooted in scientific principles and practical experience, presents a paradigm shift in forest stewardship, promising enhanced forest health, increased timber production, and a plethora of ecological benefits.
By mimicking natural forest dynamics, uneven-aged management creates forests that are more resilient, diverse, and productive. It fosters a mosaic of tree ages and sizes, providing habitat for a wide range of wildlife species, sequestering carbon, and safeguarding water quality.
Moreover, it ensures a sustainable timber supply while enhancing the aesthetic value of forests and providing recreational opportunities.
Forest Health and Biodiversity
Uneven-aged management promotes forest health by maintaining a diverse range of tree species and age classes. This diversity reduces the risk of pest outbreaks and disease spread, as different species have different susceptibilities to these threats. Additionally, uneven-aged forests have a more complex structure, with multiple layers of vegetation that provide habitat for a wider variety of plant and animal species.
Supporting Plant and Animal Diversity
Uneven-aged management supports a diverse range of plant and animal species by providing a variety of habitats. For example, older trees provide nesting sites for birds and cavities for small mammals, while younger trees provide food and cover for deer and other wildlife.
The structural complexity of uneven-aged forests also creates microclimates that support a wider range of species.
Mitigating Climate Change Impacts
Uneven-aged management can mitigate the impacts of climate change by increasing forest resilience and carbon sequestration. The diverse tree species and age classes in uneven-aged forests make them more resistant to drought, storms, and other climate-related disturbances. Additionally, uneven-aged forests have a higher biomass than even-aged forests, which means they store more carbon dioxide.
Timber Production

Uneven-aged management can provide economic benefits for timber production by increasing the value and quality of timber. The diversity of tree species and age classes in uneven-aged forests allows for selective harvesting, which can target specific trees or species based on their market value.
Additionally, uneven-aged management promotes the growth of high-quality timber by reducing competition and providing more light and nutrients to individual trees.
Increasing Timber Value and Quality
Uneven-aged management increases the value and quality of timber by promoting the growth of high-quality trees. The selective harvesting of mature trees allows younger trees to grow without competition, which results in straighter, more valuable timber. Additionally, the diversity of tree species in uneven-aged forests allows for the production of a wider range of timber products, which can increase the overall value of the forest.
Long-Term Sustainability
Uneven-aged management is a more sustainable approach to timber production than even-aged management. The continuous regeneration of trees in uneven-aged forests ensures a steady supply of timber without depleting the forest’s resources. Additionally, the diversity of tree species and age classes in uneven-aged forests makes them more resilient to pests, diseases, and other disturbances, which can reduce the risk of catastrophic losses.
Recreation and Aesthetics
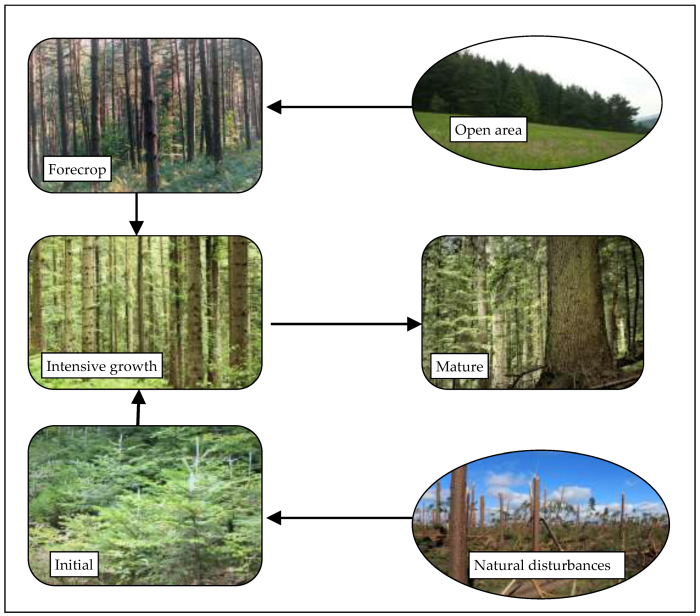
Uneven-aged forests provide a variety of recreational opportunities, including hiking, camping, fishing, and wildlife viewing. The structural complexity and diversity of uneven-aged forests create a more aesthetically pleasing environment than even-aged forests, which can attract visitors and promote forest-based tourism.
Recreational Opportunities, Why is uneven-aged management a better way to manage forests
Uneven-aged forests provide a variety of recreational opportunities because they offer a diverse range of habitats and scenic beauty. The structural complexity of uneven-aged forests creates a more challenging and interesting environment for hikers and mountain bikers, while the diversity of tree species and age classes provides habitat for a wide range of wildlife, making them ideal for wildlife viewing.
Aesthetic Value
Uneven-aged forests are generally considered to be more aesthetically pleasing than even-aged forests. The diversity of tree species and age classes creates a more visually interesting environment, with a variety of colors, textures, and shapes. Additionally, the structural complexity of uneven-aged forests provides a sense of depth and mystery, which can be appealing to visitors.
FAQ Section: Why Is Uneven-aged Management A Better Way To Manage Forests
What are the primary advantages of uneven-aged management?
Uneven-aged management promotes forest health, supports biodiversity, increases timber value and quality, provides recreational opportunities, and enhances watershed protection.
How does uneven-aged management contribute to climate change mitigation?
Uneven-aged forests sequester more carbon than even-aged forests and provide a more resilient ecosystem in the face of climate change impacts.
What wildlife species benefit from uneven-aged management?
Uneven-aged forests provide habitat for a diverse range of wildlife species, including birds, mammals, amphibians, and reptiles.