Embark on a captivating journey into the realm of chemical bonds, where the “Type of Bond in Chemistry Crossword” unveils the intricacies of molecular interactions. This comprehensive guide delves into the fundamental principles of chemical bonding, exploring the diverse types of bonds that govern the behavior and properties of matter.
From the enigmatic nature of covalent bonds to the electrostatic forces of ionic bonds, this discourse unravels the secrets of chemical connectivity. Prepare to witness the dance of electrons, the formation of molecules, and the remarkable forces that shape our physical world.
Chemical Bonding in Chemistry

Chemical bonding refers to the attractive forces that hold atoms together to form molecules and compounds. It is the fundamental concept that determines the structure, properties, and reactivity of chemical substances.
Types of Chemical Bonds
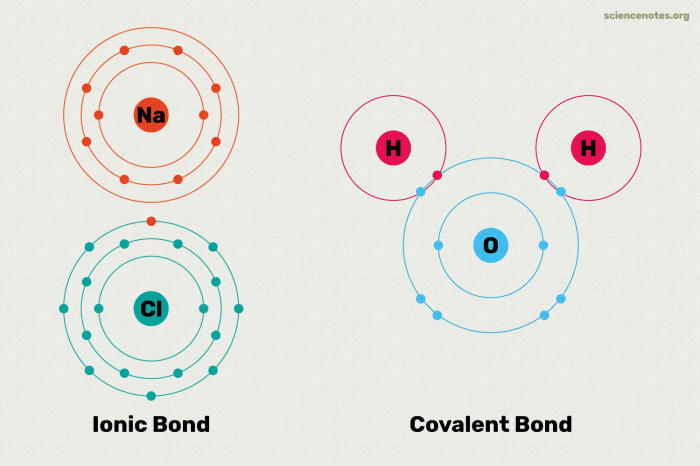
- Covalent Bonds: Covalent bonds are formed when atoms share one or more pairs of electrons. They are the strongest type of chemical bond and are commonly found in organic compounds.
- Ionic Bonds: Ionic bonds are formed when one atom transfers one or more electrons to another atom, creating oppositely charged ions that attract each other. They are typically found in inorganic compounds.
- Hydrogen Bonds: Hydrogen bonds are weak attractive forces that occur between a hydrogen atom bonded to an electronegative atom (such as oxygen, nitrogen, or fluorine) and another electronegative atom. They play a crucial role in biological systems and in determining the properties of water.
- Metallic Bonds: Metallic bonds are formed between metal atoms in a metal lattice. They are characterized by high electrical and thermal conductivity and malleability.
- Intermolecular Forces: Intermolecular forces are weaker attractive forces that occur between molecules, such as van der Waals forces, dipole-dipole interactions, and London dispersion forces. They determine the physical properties of substances, such as melting point and boiling point.
Covalent Bonds
Covalent bonds are formed when atoms share electrons to achieve a stable electron configuration. The shared electrons are attracted to the nuclei of both atoms, creating a strong bond. Covalent bonds can be single, double, or triple, depending on the number of shared electron pairs.
Ionic Bonds
Ionic bonds are formed when one atom transfers electrons to another atom, creating oppositely charged ions. The electrostatic attraction between the ions holds the compound together. Ionic bonds are typically strong and brittle, and they are found in many inorganic compounds, such as sodium chloride (NaCl).
Hydrogen Bonds, Type of bond in chemistry crossword
Hydrogen bonds are weak attractive forces that occur between a hydrogen atom bonded to an electronegative atom and another electronegative atom. The electronegative atom attracts the electron cloud of the hydrogen atom, creating a partial positive charge on the hydrogen atom and a partial negative charge on the electronegative atom.
This electrostatic attraction forms the hydrogen bond.
Metallic Bonds
Metallic bonds are formed between metal atoms in a metal lattice. The metal atoms lose their valence electrons, which become delocalized and move freely throughout the lattice. This sea of delocalized electrons holds the metal atoms together, creating a strong and ductile bond.
Intermolecular Forces
Intermolecular forces are weaker attractive forces that occur between molecules. They are responsible for the physical properties of substances, such as melting point and boiling point. The strength of intermolecular forces depends on the polarity of the molecules and the size and shape of the molecules.
Commonly Asked Questions: Type Of Bond In Chemistry Crossword
What is the fundamental concept behind chemical bonding?
Chemical bonding arises from the attraction between atoms or ions, driven by the desire to achieve a more stable electronic configuration.
How do covalent bonds differ from ionic bonds?
Covalent bonds involve the sharing of electrons between atoms, while ionic bonds result from the electrostatic attraction between oppositely charged ions.
What is the significance of hydrogen bonds in biological systems?
Hydrogen bonds play a crucial role in stabilizing the structures of proteins and nucleic acids, enabling their essential functions in biological processes.