Counting atoms in chemical formulas worksheet – Counting atoms in chemical formulas is a fundamental skill in chemistry that enables the precise determination of the elemental composition and stoichiometry of chemical reactions. This comprehensive worksheet provides a step-by-step guide to counting atoms in chemical formulas, emphasizing the significance of accurate calculations for understanding chemical processes.
Understanding the principles of counting atoms empowers chemists with the ability to analyze chemical formulas, determine the number of atoms of each element present, and establish the ratios of reactants and products involved in chemical reactions.
Counting Atoms in Chemical Formulas: Counting Atoms In Chemical Formulas Worksheet
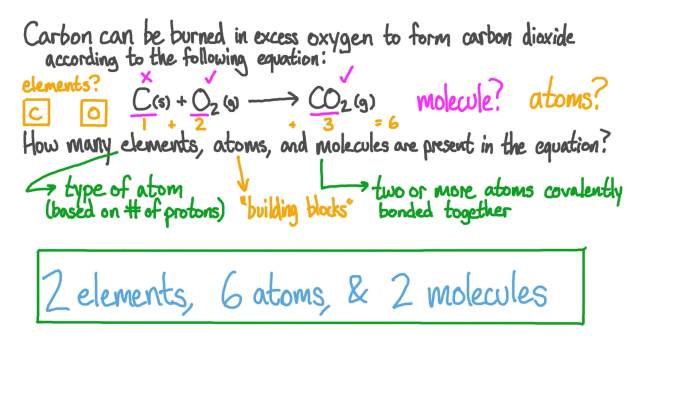
Counting atoms in chemical formulas is crucial for understanding chemical reactions and stoichiometry. It helps determine the ratios of reactants and products, which is essential for predicting the outcome of chemical processes.
There are several methods for counting atoms in chemical formulas, including using subscripts and coefficients. Subscripts indicate the number of atoms of a particular element in a molecule, while coefficients indicate the number of molecules of a particular compound.
Methods for Counting Atoms
- Using Subscripts:Each subscript in a chemical formula represents the number of atoms of the corresponding element in a molecule. For example, in the formula H 2O, the subscript 2 indicates that there are two atoms of hydrogen for every one atom of oxygen.
- Using Coefficients:Coefficients are numbers placed in front of chemical formulas to indicate the number of molecules of that compound involved in a reaction. For example, in the equation 2H 2+ O 2→ 2H 2O, the coefficient 2 in front of H 2indicates that two molecules of hydrogen are required to react with one molecule of oxygen.
Importance of Counting Atoms, Counting atoms in chemical formulas worksheet
Counting atoms in chemical formulas is essential for understanding chemical reactions and stoichiometry. It helps determine the ratios of reactants and products, which is crucial for predicting the outcome of chemical processes.
For example, in the reaction 2H 2+ O 2→ 2H 2O, counting the atoms of each element ensures that the number of atoms of each element is the same on both sides of the equation. This is known as the law of conservation of mass, which states that matter cannot be created or destroyed in a chemical reaction.
Practice Problems
Practice counting atoms in the following chemical formulas:
- NaCl
- C6H 12O 6
- Fe 2O 3
- CH 3OH
- CaCO 3
Applications in Chemistry
Counting atoms in chemical formulas has numerous applications in chemistry, including:
- Chemical Synthesis:Determining the number of atoms in a chemical formula is crucial for synthesizing new compounds. By counting the atoms, chemists can ensure that the correct ratios of reactants are used to obtain the desired product.
- Drug Development:Counting atoms in drug molecules is essential for understanding their structure and properties. This information helps researchers design and develop new drugs with improved efficacy and safety.
- Environmental Analysis:Counting atoms in environmental samples helps determine the concentration of pollutants and monitor the health of ecosystems.
Question Bank
What is the importance of counting atoms in chemical formulas?
Counting atoms in chemical formulas is essential for determining the elemental composition and stoichiometry of chemical reactions. It enables chemists to establish the ratios of reactants and products, predict the outcome of reactions, and understand the behavior of chemical substances.
What are the different methods for counting atoms in chemical formulas?
The most common methods for counting atoms in chemical formulas involve using subscripts and coefficients. Subscripts indicate the number of atoms of a particular element within a molecule, while coefficients represent the number of molecules of a compound involved in a reaction.
How does counting atoms help in understanding chemical reactions?
Counting atoms in chemical formulas allows chemists to determine the stoichiometry of reactions, which is the quantitative relationship between the reactants and products. By understanding the stoichiometry, chemists can predict the amount of reactants and products involved in a reaction, as well as the limiting reagent and the theoretical yield.
